WHAT IS SIX SIGMA?
- To deliver the TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT services in a minimum rate locally and globally for different segment with intelligence, integrity and consistency.
- There are various courses listed below will be delivered to candidates.
Six Sigma is a method that provides organizations tools to improve the capability of their business processes. This increase in performance and decrease in process variation helps lead to defect reduction and improvement in profits, employee morale, and quality of products or services.
“Six Sigma quality” is a term generally used to indicate a process is well controlled (within process limits ±3s from the center line in a Control Charts and requirements/tolerance limits ±6s from the center line).
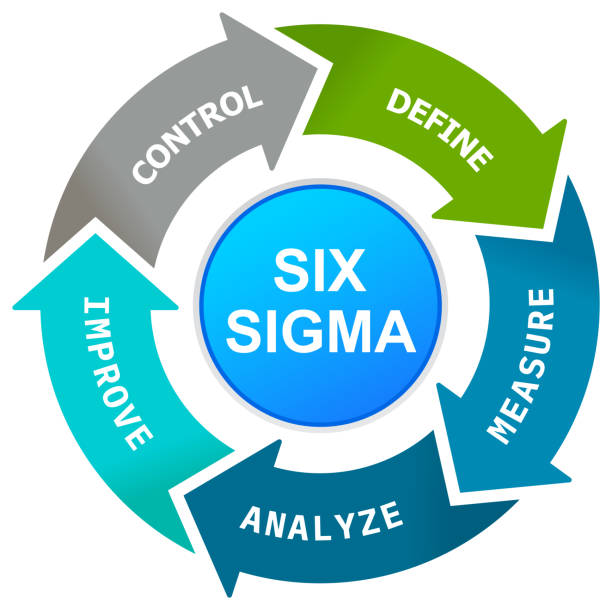
DIFFERING OPINIONS ON THE DEFINITION OF SIX SIGMA
The differing definitions below have been proposed for Six Sigma, but they all share some common threads:
- The use of teams that are assigned well-defined projects that have a direct impact on the organization’s bottom line.
- Training in “statistical thinking” at all levels and providing key people with extensive training in advanced statistics and project management. These key people are designated “Black Belts.” . Review of different Six sigma belts.
- Emphasis on the DMAIC approach to problem solving: define, measure, analyze, improve, and control.
- A management environment that supports these initiatives as a business strategy.
Set of tools: The Six Sigma expert uses qualitative and quantitative techniques or tools to drive process improvement. Such tools include, Statistical process control , Control Charts, Failure mode effect analysis, Process mapping. Six Sigma professionals do not totally agree as to exactly which tools constitute the set.
Methodology: This view of Six Sigma recognizes the underlying and rigorous DMAIC approach. DMAIC defines the steps a Six Sigma practitioner is expected to follow, starting with identifying the problem and ending with the implementation of long-lasting solutions. While DMAIC is not the only Six Sigma methodology in use, it is certainly the most widely adopted and recognized.
Metrics: In simple terms, Six Sigma quality performance means 3.4 defects per million opportunities (accounting for a 1.5-sigma shift in the mean).
